Original Articles: 2025 Vol: 17 Issue: 1
Pharmacological Activities of a Synthesized Schiff Base and its Polymer Complexes
Salman Alotaibi*
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Qassim University, Buraidah 51452, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding Author:
- Salman Alotaibi
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Qassim University, Buraidah 51452, Saudi Arabia
Received: 06-Nov-2023, Manuscript No. JOCPR-23-119362; Editor assigned: 08-Nov-2023, PreQC No. JOCPR-23-119362 (PQ); Reviewed: 22-Nov-2023, QC No. JOCPR-23-119362; Revised: 03-Jan-2025, Manuscript No. JOCPR-23-119362 (R); Published: 13-Jan-2025, DOI:10.37532/0975-7384.2025.17(1).234.
Citation:Alotaibi S. 2025. Pharmacological Activities of a Synthesized Schiff Base and its Polymer Complexes. J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 17:140.
Copyright: © 2025 Alotaibi S. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
A Schiff base was prepared via condensation reaction of 4-chlorobenzaldehyde, 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and p-phenylenediamine, and its Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) polymeric complexes were obtained in similar manner. 1H and 13CNMR, FT-IR, UV-Vis, CHN, ICP, and conductivity measurements were utilized for structural investigation. The 1HNMR confirmed the formation of the azomethine by detecting two singlet peaks of the protons that are associated with C=N groups, and the peaks related to the carbons of the azomethine groups were revealed by 13CNMR. The FT-IR also disclosed sharp strong bands at 1680 and 1537 cm-1 in the spectrum of the SB ligand, and in the spectra of the polymeric complexes these bands shifted to higher or lower frequencies, proving the coordination to the ligand. The UV-Vis has clearly shown abroad absorption bands at 255 and 339 nm for the synthesized SB ligand, accredited to the π → π* transitions of the C=C aromatic rings and n → π* transitions of C=N azomethine groups. These transitions have also shifted to higher or lower frequencies in the UV-Vis spectrum of the polymeric complexes, affirming their formation. Moreover, it was determined that the polymeric complexes possess an octahedral geometry shapes, which were detected by the d-d transitions in the UV-Vis spectrum. The polymeric Cu(II) and Ni(II) complexes were tested for their antibacterial activities, and had shown a potent effect against Salmonella typhi.
Keywords
Salmonella typhi, Azomethine, Hydroxybenzaldehyde, Phenylenediamine, Chlorobenzaldehyde
Introduction
In recent years, the development of innovative materials with enhanced antibacterial properties has emerged as a critical area of research in the field of polymer science and medicinal chemistry. Among the various classes of compounds investigated for their antibacterial potential, Schiff base complexes have garnered significant attention due to their versatile coordination chemistry and ability to form stable complexes with a wide range of metal ions [1]. The incorporation of Schiff base ligands into polymeric complexes has yielded a class of materials known as polymer complexes of Schiff base, which exhibit remarkable antibacterial activity against pathogenic microorganisms [2–3].
Schiff bases, derived from the condensation of aldehydes or ketones with primary amines, possess unique structural features that contribute to their antibacterial efficacy. These compounds often contain functional groups with electron-donating or withdrawing properties, which play a crucial role in their interactions with bacterial cells. Additionally, the presence of metal ions in the polymer complex further enhances the antibacterial activity through mechanisms such as chelation, disruption of bacterial cell walls, and interference with enzymatic processes [4].
The design and synthesis of polymer complexes of Schiff bases with antibacterial activity involve the careful selection of both the Schiff base ligand and the metal center. Tailoring the chemical structure of the ligand allows for the optimization of antibacterial properties, including selectivity, potency, and spectrum of activity. Furthermore, the choice of metal ion can influence the mode of action and overall effectiveness of the polymer complex against specific bacterial strains [5].
This study aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the synthesis strategies, structural features, and antibacterial mechanisms of polymer complexes of Schiff base, which is 2-((E)-((4-((E)-(4-chlorobenzylidene)amino)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenol (prepared from p-phenylenediamine, salicylaldehyde and 4-chlorobenzaldehyde), is the structural and biological activity (antibacterial), and its polymeric Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes. 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, CHN elemental analysis, and molar conductivity measurements, were employed for structural determinations.
Materials and Methods
Experimental section
Materials and instrumentation: The following chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Fluka, and E. Merck and used as obtained: 4-chlorobenzaldehyde, 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and p-phenylenediamine, as well as the appropriate metal salts (CuCl2.2H2O, CoCl2.6H2O, and NiCl2.6H2O). Absolute ethanol and DMSO were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich for the synthesis of the Schiff base ligand and its metal complexes without any further purification. 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy of the Schiff base ligand was performed on Bruker 850 MHz and 213 MHz spectrometers, respectively, using DMSO-d6. An Agilent spectrometer was used to register transmission spectra in the region 4000-400 cm−1. Electronic UV-Visible spectra were recorded using the Shimadzu spectrophotometer (UV-1650PC, Japan). C, H and N analyses were performed using Eurovector CHN Elemental Analyzer (EA3000, Italy). Metal percentages were measured using Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP 710-ES Varian). Conductivity/DTS Meter was put to measure the molar conductivity. The melting points of SB ligand and its complexes were determined in open capillary tubes using Stuart SMP30 Apparatus.
Synthesis of the Schiff base
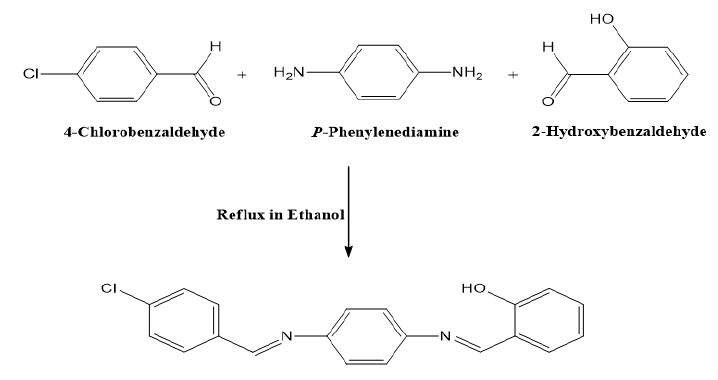
The following method was used to prepare the SB ligand under study, 2-((E)-((4-((E)-(4-chlorobenzylidene)amino) phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol. A solution of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (0.590 g; 5 mmol) and 4-chlorobenzaldehyde (0.703 g; 5 mmol) in 20 mL absolute ethanol were gradually added to a stirred mixture of p-phenylenediamine (0.540 g; 5 mmol) in hot absolute ethanol (15 mL) solution. The mixture's color changed from brown to yellow after being refluxed with heating for four hours and stirred without heating for the entire precipitation. The yellow product that had precipitated was then isolated by filtration, washed numerous times with hot absolute ethanol, and vacuum-dried. Yield: 91.7%. Decomposition point: 160°C. 1H NMR (850.000 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm): 13.0 (s, 1H, Ar-OH), 9.0 (s, 1H, HC=N), 8.9 (s, 1H, HC=N), 8.3-6.9 (m, 12H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (213.77 MHz, DMSO-d6) (δ, ppm): 162.1–11.8. IR, v(cm−1): 3100(O-H), 1680(C=N), 1537(C=N), 1245(C-O). UV-Vis (DMSO), λmax (nm): 255 (π → π*), 339 (n→π*). Elemental Analysis (%) For C20H15ClN2O Calculated: C: 71.76, H: 4.38, N: 12.17; Cl. 10.59. Found: C: 71.75, H: 4.37, N: 12.17, Cl: 12.59 Molar conductance (DMSO): 4.7 Ω−1.mol−1.cm2.
Synthesis of the Schiff base polymeric transition metal complexes
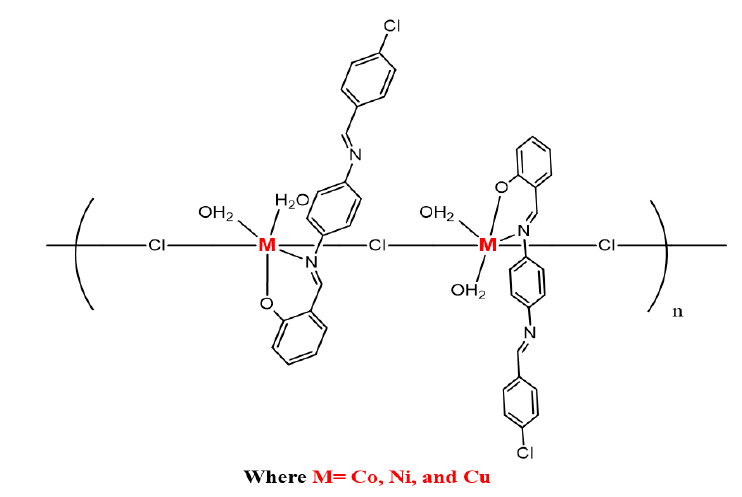
All complexes were synthesized in a similar manner. To a stirred solution of the synthesized ligand of (0.690 g, 2 mmol) in hot absolute ethanol (20 mL), the appropriate metal salts, CuCl2.2H2O (0.340, 2 mmol), CoCl2.6H2O (0.476 g, 2 mmol), and NiCl2.6H2O (0.476 g, 2 mmol in hot absolute ethanol (15 mL), were added separately. The solutions were refluxed for 3 h for complete precipitation. Then, the products were washed with absolute ethanol several times and dried by vacuum.
[Ni2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n
Yield: 87.3 %. Decomposition Point: 250 °C. IR, v(cm−1): 1672 (C=N), 1543 (C=N), 1240 (C-O), 520 (M-O), 460 (M-N). UV-Vis (DMSO), λmax (nm): 260 (π → π*), 325 (n→π*), 510, 588. Elemental analysis (%): calculated for [Ni2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]: C: 53.82, H: 4.36, N: 5.78, Cl: 14.62, Ni: 12.10; Found: C: 53.20, H: 4.36, N: 5.76, Cl: 14.62, Ni: 12.09. Molar conductance (DMSO): 8.9 Ω−1.mol−1.cm2.
[Cu2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n
Yield: 89.8 %. Decomposition Point: >300°C. IR, v(cm−1): 1675 (C=N), 1535 (C=N), 1253 (C-O), 519 (M-O), 433 (M-N). UV-Vis (DMSO), λmax (nm): 242 (π → π*), 340 (n→π*), 560. Elemental analysis (%): calculated for [Cu2L2Cl2 (H2O)4], C: 53.72, H: 4.32, N: 5.72, Cl: 14.47, Cu: 12.97; Found: C: 53.72, H: 4.32, N: 5.72, Cl: 14.47, Cu, 12.13. Molar conductance (DMSO): 11.6 Ω−1.mol−1.cm2.
[Co2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n
Yield: 95.3%. Decomposition Point: 290°C. IR, v(cm−1): 1682 (C=N), 1525 (C=N), 1255 (C-O), 527 (M-O), 440 (M-N). UV-Vis (DMSO), λmax (nm): 238 (π → π*), 329 (n → π*), 368, 580. Elemental analysis (%): calculated for [Co2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]: C: 53.22, H: 4.36, N: 5.77, Cl: 14.61, Co: 12.14; Found: C: 53.23, H: 4.36, N: 5.77, Cl: 14.61, Co: 12.13. Molar conductance (DMSO): 13.4 Ω−1.mol−1.cm2.
Antibacterial activity
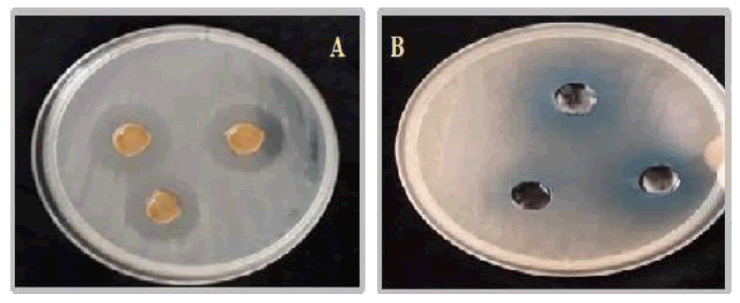
Employing the hole plate diffusion technique, the Schiff base ligand, along with its Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes, were diluted using DMSO to achieve concentrations of 100 Parts Per Thousand (PPT). Subsequently, their antibacterial properties were assessed against Salmonella typsshi [6–7]. Various quantities of each compound (30, 20, and 10 μL) were introduced into individual wells in the Petri dish using a sterile micropipette tip. Gentamicin (10 μg/mL) was utilized as the positive control.
Results and Discussion
Chemistry
After the successful formation of synthesizing the SB ligand, following seven’s procedure [8], and its polymer complexes of Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II), it was determined that the polymeric complexes were insoluble in water while they were moderately soluble in organic solvents like MeOH, EtOH, DMF, and DMSO, which could be concluded that the complexes possess polymeric nature. Figures 1 and 2 present the final obtained structure of SB ligand and its polymeric complexes.
1H and 13C NMR
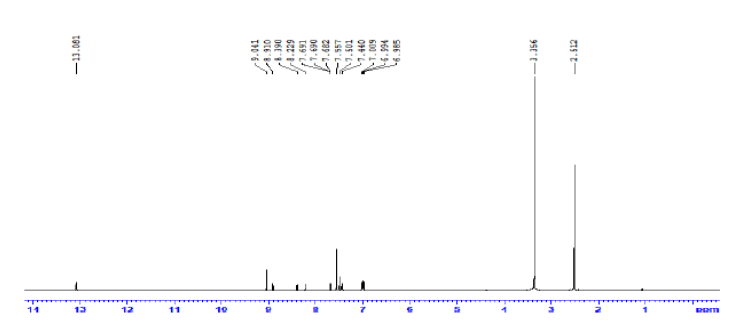
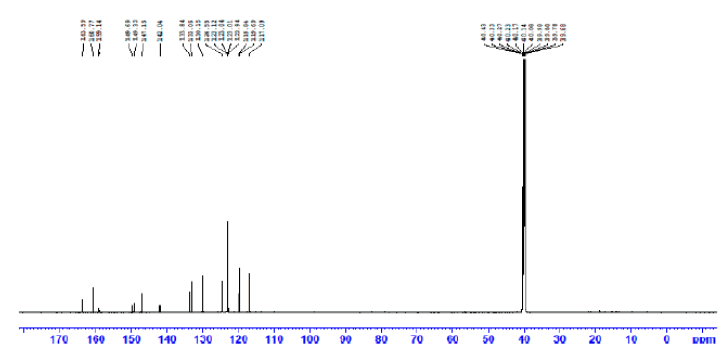
The 1HNMR spectrum of the Schiff base assured the proposed structure of the synthesized SB ligand. The aromatic protons of the ligand are discerned within the projected chemical shift range of 6.9–8.3 ppm, manifested as complex multiplets [9]. Notably, two peaks at 8.9 and 9.0 ppm are assignable to the HC=N protons [10], while a singlet at 13.0 ppm in the downfield region is indicative of the phenolic proton [9–10]. On the other hand, In the 13C NMR, distinctive peaks emerged at 163.7 ppm, 160.8 ppm, and 159.1 ppm, assigned to the phenolic, azomethine, and azomethine carbons, respectively. Furthermore, signals within the chemical shift range of 117.09–149.69 ppm are referred to the aromatic carbons (Figures 3 and 4) [10].
FT-IR spectroscopy
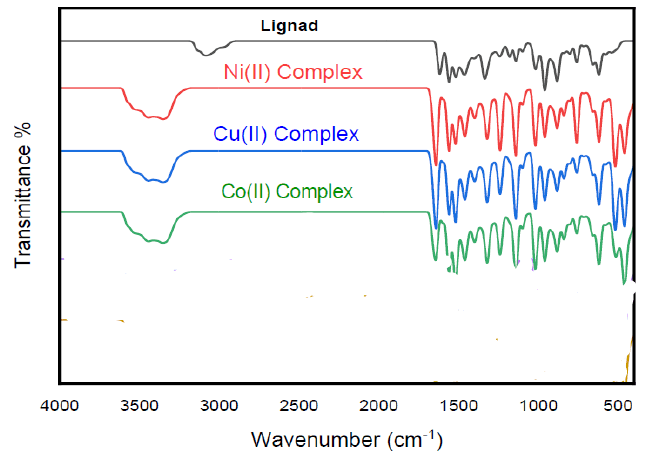
The IR spectral analyses of the Schiff base ligand and the resulting polymeric metal complexes are reported in Table 1. The high-intensity absorption bands located at 1680 and 1537 cm-1 in the Schiff base ligand spectra are unequivocally ascribed to the stretching modes of the azomethine moieties [9–10]. Meanwhile, the discernible broad absorption at 3100 cm-1, attributed to the phenolic group in the unbound SB ligand, is evident [10]. Noteworthy shifts in the band positions characteristic of the C=N stretching modes, consistently observed across all complex spectra, manifested the complexation of azomethine groups to the transition metal ions [9].
Furthermore, the emergence of new, broad absorptions in the complexes, in the range of 3600–3300 cm-1, are ascribed to the symmetric and asymmetric stretching modes of coordinated water molecules [11]. Additionally, the distinctive band associated with the C-O stretching mode, is observed at 1245 cm-1 in the free Schiff base, undergoes a notable shifts in the IR spectra of the metal complexes, affirming the deprotonation and the consequent formation of phenolate-type coordinated Schiff base-transition metal complexes [10]. The respective M-O bands appeared in the spectral region of 510–523 cm-1, while the M-N bands are distinctly observed within the range of 440–460 cm-1 [12].
| Compound | v(OH) cm-1 | v(C=N) cm-1 | v(C-O) cm-1 | v(M-O) cm-1 | v(M-N) cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L=C20H15ClN2O | 3100 | 1680-1537 | 1245 | - | - |
| [Ni2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | - | 1672-1543 | 1240 | 520 | 460 |
| [Cu2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | - | 1675-1535 | 1253 | 519 | 433 |
| [Co2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | - | 1682-1525 | 1255 | 527 | 440 |
Table 1: Characteristic IR absorption bands (cm-1) of the prepared Schiff base ligand and its metal (II) and Metal (III) complexes.
CHN analyses
All the data obtained from the CHN elemental analyzer were in good agreement with the proposed structures and the calculated values of the C, H, and N content. The found values were in agreement with the expected values (Table 2). The ICP confirmed the percentage of the metal present in the complexes, and the chloride analysis is in good agreement with theoretical values of the proposed structure.
| Compound | D.P. (°C) | M | C | H | N | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated (Found) (%) | ||||||
| L=C20H15ClN2O | 160 | - | 71.76 (71.75) | 4.38 (4.37) | 12.17 (12.15) | 10.59 (12.59) |
| [Ni2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | 250 | 12.10 (12.09) | 53.82 (53.20) | 4.36 (4.36) | 5.78 (5.76) | 14.62 (14.62) |
| [Cu2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | >300 | 12.97 (12.97) | 53.72 (53.72) | 4.32 (4.32) | 5.72 (5.72) | 14.47 (14.47) |
| [Co2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | 290 | 12.14 (12.13) | 53.22 (53.23) | 4.36 (4.36) | 5.77 (5.77) | 14.61 (14.61) |
Table 2: Analytical and physical data of Schiff base and its polymeric complexes.
Electronic (UV-Visible) spectra
The UV-Visible (UV-Vis) spectrum of each compound was recorded in DMSO (1 × 10−4 M) (Table 3). The spectrum of the SB ligand exhibits bands at 255 and 339 nm, which are ascribed to the π → π* transitions of the C=C aromatic rings and n → π* transitions of C=N azomethine groups, respectively [13–14]. These bands were shifted in the spectra of metal complexes, which can be attributed to the metal-ligand coordination [13]. The electronic spectra of the Ni(II) complex show d-d transitions at 510 and 588 nm, the Co (II) complex shows at 560 nm, and the Cu(II) complexes shows at 690 nm, which were all in the characteristics of octahedral arrangements in all three polymeric complexes [15].
| Compound | Volumes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 μL | 20 μL | 10 μL | Gentamycin (10 μg/mL) positive control | |
| L=C20H15ClN2O | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| [Ni2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | 11 | 9 | 7 | |
| [Cu2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | 13 | 11 | 8 | |
| [Co2L2Cl2 (H2O)4]n | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Table 3: Antibacterial activities of the Schiff base ligand and its Polymeric complexes.
Molar conductivity
The molar conductivities (10−3 M) of the prepared polymeric complexes dissolved in DMSO were determined at room temperature. The molar conductivities of the synthesized polymeric complexes were found in the range 8.9, 11.6 and 13.4 Ω−1.mol−1.cm2 for the Ni(II), Cu(II) and Co(II) complexes, which signify the none electrolyte nature [13,16]. Also, it was figured out that all chlorine ions are involved in coordinating with the metals and not located outside the coordination sphere by adding AgNO3 solution to the complexes, which indicated that no white precipitate has formed [13].
Antibacterial activity
Table 3 presents the Schiff base ligands along with their respective complexes, detailing their in vitro antibacterial activity against Salmonella typhi. The Cu(II) complex exhibited pronounced activity at a sample volume of 30 μL, while demonstrating intermediate activity at sample volumes of 20 μL and 10 μL. Conversely, the Ni(II) complex displayed intermediate activity across all sample volumes (30 μL, 20 μL and 10 μL). It is noteworthy that both the Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes exhibited superior antibacterial properties compared to the free Schiff base ligand.
Conclusion
In this study, a successful synthesis of Schiff base and its polymeric Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes has been performed. Instrumental characterization were done by 1H and 13C NMR, FT-IR, UV-Vis, CHN, ICP, and Conductivity. It could be concluded that the instruments confirmed the polymeric complexes. Finally, the antibacterial activity showed and excellent result for the Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes.
References
- Chandra D, et al. Int J Chem Tech Res. 2010;2(4):2035-2052.
- Bara H, et al. Medicinal Chem. 2008;4(6):618-632.
- Hegazi AF. J Applied Polymer Sci. 2010;116(4):1804-1813.
- Allam NM, et al. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2011;6(9):4194-4210.
- Joshi SS, et al. J Serbian Chem Soc. 2005;70(6):767-773.
- Vanco J, et al. J Inorg Biochem. 2008;102(4):595–605.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magwa ML, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;103(1):85-89.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sevens G, et al. Bull Soc Chim Belg. 1948;57:32-49.
- Aggoun D, et al. Polyhedron. 2020;187:114640.
- Abdel Aziz AA, et al. J Mol Struct. 2012;1010:130-138.
- Aroua LM, et al. Arab J Chem. 2022;15:103986.
- Howsaui HB, et al. Appl Sci. 2021;11(19):9067.
- Alorini TA, et al. Arab J Chem. 2022;15:103559.
- M Mesbah, et al. J Mol Struct. 2018;1151:41-48.
- Al-Fakeh MS, et al. Crystals. 2023;13:1148.
- Jayaseelan P, et al. Arab J Chem. 2016;9:S668–S677.